The Essential Roles of Biglycan and Decorin in Bone Health
January 11, 2025 - 07:23
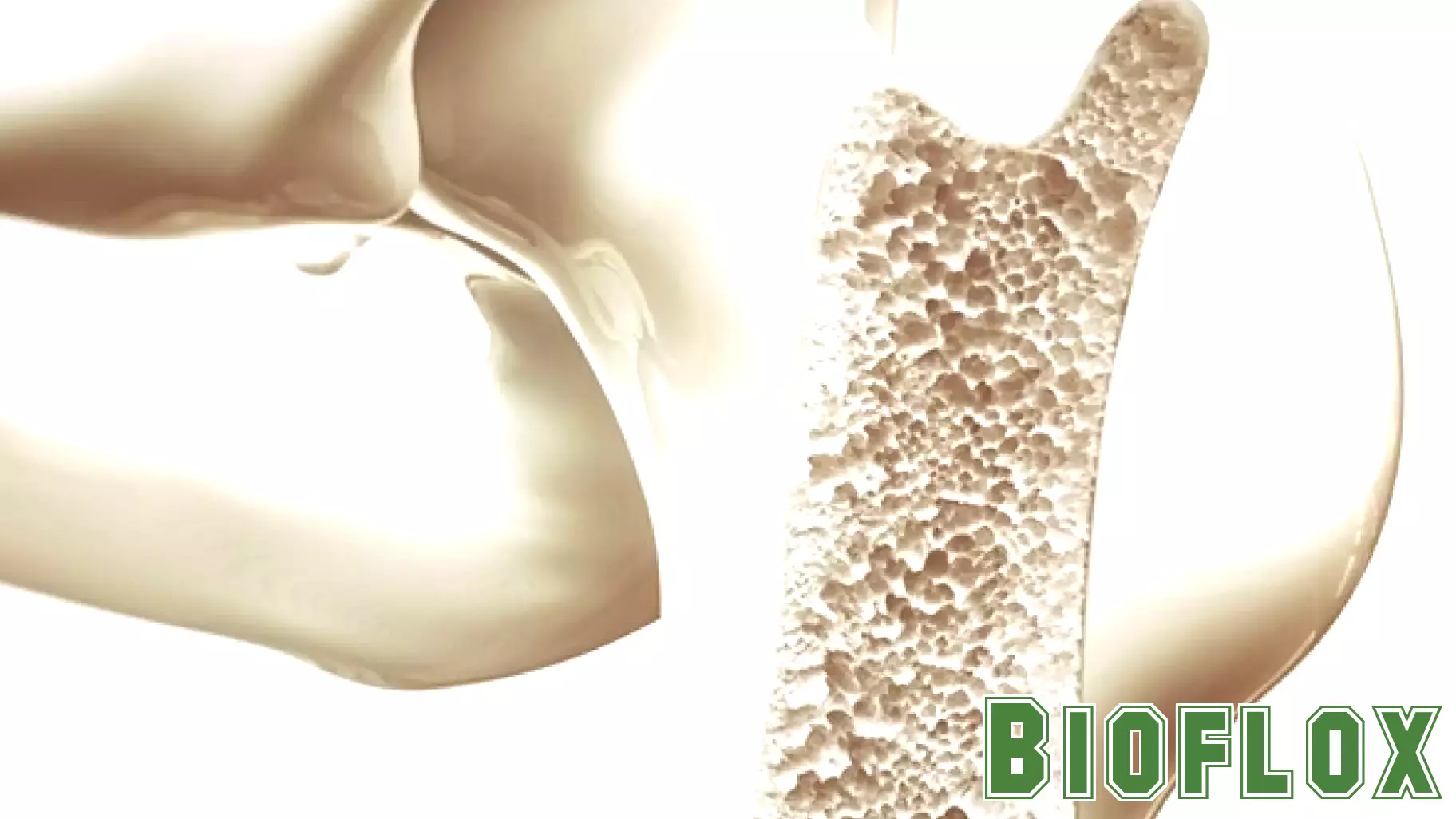
Bone tissue is a complex structure, consisting of mineralized collagen fibers and a variety of non-collagenous proteins, including proteoglycans such as biglycan and decorin. Recent studies have highlighted the critical functions these proteoglycans serve in maintaining bone integrity and health.
Biglycan and decorin are known to influence the organization of collagen fibers, which is essential for the mechanical strength of bones. They also play a vital role in regulating mineralization, ensuring that bones acquire the necessary density and resilience. Additionally, these proteoglycans contribute to the signaling pathways that govern bone formation and resorption, making them key players in the balance of bone remodeling.
Deficiencies in biglycan and decorin have been linked to various bone disorders, including osteoporosis, underscoring their importance in skeletal health. Understanding the mechanisms through which these molecules operate could pave the way for new therapeutic strategies aimed at enhancing bone health and preventing related diseases. Continued research into these proteoglycans promises to shed light on their multifaceted roles in skeletal biology.
MORE NEWS

March 12, 2026 - 04:36
Jamie Erdahl away from NFL Network for 'tragic' family health matterJamie Erdahl, the beloved host of NFL Network`s `Good Morning Football,` has taken an indefinite leave of absence from the program due to a serious family health situation. The network confirmed...

March 11, 2026 - 02:56
Simulation Training Featured in New Episode of NYC Health + Hospitals Podcast The Remedy - NYC Health + HospitalsNew York, NY – A new podcast episode is shedding light on the cutting-edge simulation technology transforming how healthcare professionals train within the city`s public hospital system. The...

March 10, 2026 - 13:09
Cancer Haunts Neighbors of Canada’s Oil Sands WastelandsPersistent, elevated cancer rates in Indigenous communities downstream from Canada`s vast oil sands operations are fueling renewed controversy as federal authorities consider new industrial waste...

March 9, 2026 - 21:02
Concerns Raised Over Accuracy of Affordable Care Act Enrollment FiguresA senior health official has sparked debate by suggesting that enrollment numbers within the Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplaces may be inflated. The comments point to potential issues with...